~ 2 min read
The Road to Node.js ES6

So you’re interested in writing up some ES6 on your server-side Node.js project? awesome! you’re in the right place.
Node.js ES6 Support
Node.js follows a release plan, and currently v5 is not supported anymore, which leaves us with v4 on a Long Term Support (LTS) until 2018, and v6 a couple of years later.
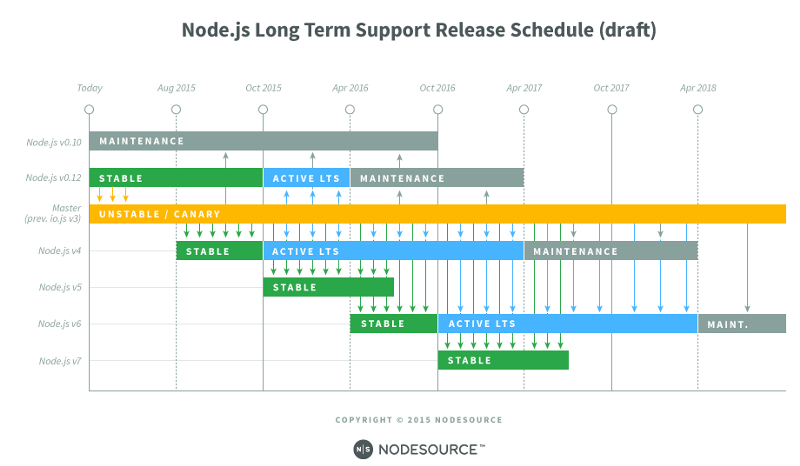
Node.js v6 has received updates recently which now makes it 99% compatible with ES6. This can be easily monitored with node.green, which if you haven’t heard of, then here’s how it looks like:

So the go-to version now should probably be the latest v6 if you can afford it in your projects (dependencies issues and such).
Ensuring ES6 Support
It’s not easy for all projects to just upgrade to Node v6, so to make this transition process easier we’re going to add a transpiler called Babel, which is actually just a fancy way of saying “let’s use a tool that compiles our ES6 code to ES5 JavaScript which is supported well by older versions”.
Gulp will be used as a build process that compiles our source code with Babel, and saves it to a build folder.
Installing required libraries which are:
- gulp itself
- gulp-babel module which bundles babel itself
- and the ES6 preset (often referred to as ES2015) which is basically a plugin that tells Babel how to translates source code for a specific language:
npm install —save gulp gulp-babel babel-preset-es2015
Compiling JavaScript with Gulp
Next up is to create the Gulp configuration which we will invoke in order to compile the code that we write in ES6 to the wider supported ES5 version of JavaScript.
gulpfile.js:
var gulp = require('gulp');
var babel = require('gulp-babel');
gulp.task('compile', function() {
return gulp.src('lib/\*.js')
.pipe(babel({ presets: \['es2015'\] }))
.pipe(gulp.dest('build'));
});The gulp configuration is pretty straightfoward, we defined a task called compile that when run it will:
- process all the
_.js_files in the_lib_directory - pipe all the javascript files to babel and tell babel to compile it with the ES6 support
- save all the files in the
_build_directory
That’s it!
You can now write ES6 in all of your source code files in the _lib_ directory, and once you run _gulp compile_ outside in the main project directory everything will be compiled into _build_.
You might want to change the gulp configuration to accommodate your project’s sources, directories, etc. Might also want to add gulp into your _package.json_ scripts and build process.
